Installing and configuring VirtualBox on Windows
Today I will talk about my experience installations, settings And configuration Virtual Box on Windows. Also, I will tell you why I chose VirtualBox virtualization platform, why do I need it at all, etc. To save your time, I suggest you watch a video on the topic:
Why Virtualbox?
Before I go into the reasons why I chose virtualbox, I would like to touch on the topic of virtualization and emulation in general. What is emulation?
Emulation is the ability of a program or device to mimic the operation of another program or device.
Who uses emulators and why?
Software emulators are primarily designed to deploy multiple operating systems on a single computer without affecting the main operating system. Emulators or virtualization systems are available to a wide range of people: from ordinary users to administrators and programmers.
Emulators for users- this is, first of all, the ability to run applications for other operating systems without rebooting the main one, testing new software and various experiments with settings.
Emulators for administrators- This is a testing ground! Now administration training has become much easier, anyone can create virtual networks from dozens of guest operating systems, configure them, gaining practical skills.
Emulators for programmers- these are those assistants, without which it is already difficult to do. They speed up debugging and testing programs literally at times. And if we talk about developers of network applications or low-level programming, then emulators simply do not have a price!
Emulators for hackers- well, everything is clear here, checking exploits, testing viruses, debugging and studying other people's programs ...
Therefore, the value of emulation is difficult to overestimate. The only question is which emulator to choose?
The choice of a virtual machine depends on a number of reasons that the user determines for himself. I proceeded from the following requirements for a virtual machine:
- Must work on the platform Windows
- Must support the operation of all the most common operating systems in guest mode
These two, I would say, strict requirements are not met by all virtual machines. I have considered Virtual PC(did not fit, because only Windows-guest systems are supported) and VMWare(didn’t fit, because it’s paid software, the price of which is very high, and I don’t want to use hacked versions).
Features of VirtualBox
- Cross-platform
- Modularity
- Live migration
- USB 2.0 support when host machine devices are made available to guest OSes (proprietary version only)
- Support for 64-bit guest systems (starting from version 2.0), even on 32-bit host systems (starting from version 2.1, this requires support for processor virtualization technology)
- Support for SMP on the guest side (starting from version 3.0, this requires support for processor virtualization technology)
- Built-in RDP server as well as support for USB client devices over RDP protocol (proprietary version only)
- Experimental support for hardware 3D acceleration (OpenGL, DirectX 8/9 (using wine code) (32-bit Windows XP and Vista only)), for guest DOS/Windows 3.x/95/98/ME support for hardware 3D no acceleration provided
- Support for VMDK (VMware) and VHD (Microsoft Virtual PC) hard disk images, including snapshots (since version 2.1)
- iSCSI support (proprietary version only)
- Audio device virtualization support (AC97 or SoundBlaster 16 emulation to choose from)
- Support for various types of network interaction (NAT, Host Networking via Bridged, Internal)
- Support for a chain of saved virtual machine states (snapshots), which can be rolled back from any state of the guest system
- Shared Folders support for easy file sharing between host and guest (for Windows 2000 and later, Linux and Solaris guests)
- Support for desktop integration (seamless mode) host and guest OS
- It is possible to select the interface language (Russian-language interface is also supported)
The list is impressive, besides, version 3.2.12 was recently released, a large number of errors were fixed, they can be found on the VirtualBox developer website.
I hope the purchase Sun company Oracle will not affect the development of this great project, otherwise they like to monetize everything.
Installing VirtualBox
Used as a host system Windows Vista Ultimate SP2. The process of installing VirtualBox itself is quite trivial, everything is clear and without comments.
Next, follow the installer's instructions. At one of the stages, when installing network adapters, the current connection to the local network may be interrupted. After installation, you can start adding a guest OS. After installing VirtualBox, I advise you to change some program settings, in particular, specify the default paths for new virtual OS files, etc. This can be done in the window called by the command File -> Settings.
Configuring VirtualBox
Creating a new guest OS
To create your first virtual OS, click the "Create" button. Launch the New Virtual Machine Wizard. Following his instructions, you will need to select the family of the future virtual operating system and its version, as well as enter its name.


512 MB is enough for most OSes, but I allocated 1 GB.
Next, you will need to create a new hard drive, this is a fairly simple procedure, you just need to follow the instructions in the wizard to create new hard drives. As a result, you should get something like this:

The final step in creating a guest OS in VirtualBox
Setting up guest OS hardware in VirtualBox
You can determine the hardware of the created guest system in its "Properties". To do this, by selecting the desired guest OS, we call the command Properties command panel. After that, the properties window appears. On the left in this window, the settings sections will be indicated, and in the center of the window for their installation. All settings are intuitive and have hints.

tab General - Advanced
- Snapshot folder— path to the folder where the disk images of the guest OS will be stored. The snapshot requires a large amount of disk space, so here it is better to point to a disk where there is enough space for this
- Shared Clipboard- setting the use of the clipboard between the host system and the guest OS
- Mini toolbar- console for managing a virtual machine
tab System - Motherboard
- Load order- determines the boot order of the guest OS. I advise you to change this order after installation and put the hard drive in the first place (unless, of course, loading from other media is not so important for you)
- Disable IO APIC- advanced interrupt controller used in processors from Intel. Fully supported OS Windows.
- Enable EFI — EFI defines "boot services", which include support for a text and graphical console on various devices, buses, blocks, and file services, and runtime services such as date, time, and non-volatile memory. Used by a number of OS to boot.
tab System - Processor
- Processor(s)- configure the number of processors used by the virtual machine. “Please note that this option will only be available if hardware virtualization is supported. AMD-V or VT-x tab System - Acceleration, as well as the enabled option OI APIC tab System - Motherboard.
- Enable PAE/NX- the mode of operation of the built-in memory management unit of x86-compatible processors, which uses 64-bit page table entries (of which only 36 bits are used for addressing), with which the processor can address 64 GB of physical memory (instead of 4 GB addressed when using 32-bit tables).
tab System - Acceleration
- Enable VTx/AMD-V- use of hardware virtualization of the main processor (Your processor must support these modes or they must be enabled in BIOS)
- Enable Nested Paging — Nested Paging provides translation of the physical memory addresses of the guest OS to the physical memory addresses of the host OS
tab carriers
- In this tab, you can configure the use of external media and CD/DVDs. Note that you can use virtual disks when installing the guest OS. It is very comfortable. You can add them via Virtual Media Manager in which you can store a large number of different images and switch between them during a session in the guest system. You can call this manager like this:

Virtual Disk Manager in VirtualBox
tab Net
- Network settings will be discussed in a separate article; IN Windows XP There are drivers for Pcnet-Fast III (Am79C973), so it must be chosen.
tab COM ports
- On this tab, you can configure the use of COM ports. Now they are rarely used, so it is unlikely that anyone will need to configure them.
tab USB
- Here you need to add to the list those USB-controllers to be used by virtual systems. Be careful when starting a virtual system, the specified USB-devices stop working in the main (at least it happened to me)
tab Shared folders
- Shared folders are designed to share files between the main and guest OS
Setting up an installed Windows XP guest OS in VirtualBox
We need to install drivers for all virtual hardware components of our virtual PC. This can be done by installing add-ons:
The add-on installation wizard will start if you have enabled support for 3D, then you need to indicate this by checking the box. Answer yes to all system warnings. After installing add-ons in the virtual OS, the Internet should work.
Display integration mode
A very useful mode that allows you to manage a virtual system directly in the main one, without switching to the virtual machine window. Truly incredible functionality! Try it and you will understand everything. Keyboard shortcuts are used to switch to this mode. HOST+L, where "HOST" is the host key (right "Ctrl" by default).
Used concepts and definitions
Virtual machine(VM, from the English virtual machine) is a software and / or hardware system that emulates the hardware of a certain platform and executes programs for this platform ( target- target or guest platform) on another platform ( host- host platform, host platform)
Emulation(English emulation) - reproduction by software or hardware or their combination of the work of other programs or devices.
hypervisor(or Virtual Machine Monitor) - in computers, a program or hardware circuit that provides or allows the simultaneous, parallel execution of several or even many operating systems on the same host computer. The hypervisor also provides isolation of operating systems from each other, protection and security, sharing of resources between different running OSes, and resource management.
Guest OS— the operating system installed on the virtual machine.
Host system The operating system on which the virtual machine is running.
Information sources
- VirtualBox.org - the official VirtualBox virtual machine page
- Category:Virtualization at en.wikipedia.org
- Installing and configuring the Oracle VM VirtualBox virtualization platform - an article by Viktor Krasnukhin on OSzone.net
 How to Find Duplicate Files on Windows Easily and Remove Them
How to Find Duplicate Files on Windows Easily and Remove Them Catch Answer - a powerful calculator for solving examples and equations with the output of solution steps
Catch Answer - a powerful calculator for solving examples and equations with the output of solution steps Visual browser bookmarks - install and configure ...
Visual browser bookmarks - install and configure ...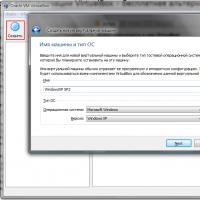 Installing and configuring VirtualBox on Windows
Installing and configuring VirtualBox on Windows com - Microsoft's cloud-based email service
com - Microsoft's cloud-based email service Visual bookmarks Top-Page
Visual bookmarks Top-Page Ways to save a password in Yandex
Ways to save a password in Yandex